The potential ethical and social challenges present in Big Data
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
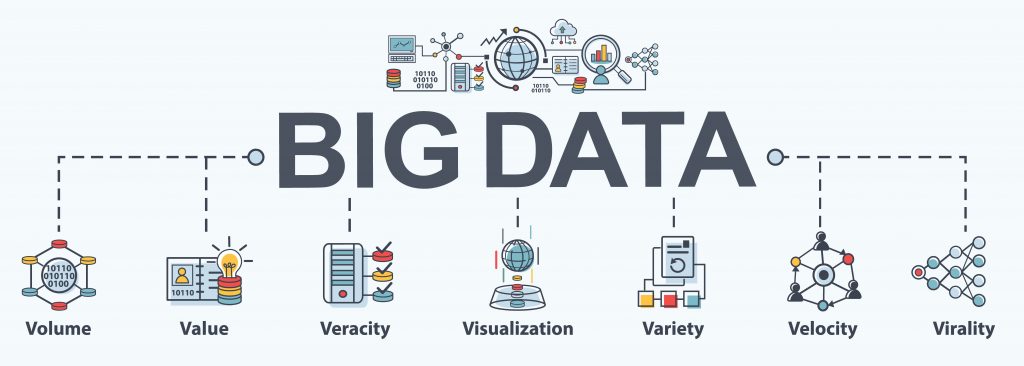
The definition of big data is data
that contains greater variety, arriving in increasing volumes and with more
velocity. This is also known as the three Vs.
Big data is composed of larger, more complex data
sets, especially from new data sources. These data sets are so voluminous that
the traditional data processing software cannot manage them.
Reference: https://www.oracle.com/ie/big-data/what-is-big-data/
Ethical Challenges
Ethics
refers to well-founded standards of right and wrong that prescribe what humans
ought to do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society,
fairness, or specific virtues.
Informed Consent
To consent
means that you give uncoerced permission for something to happen to you.
Informed
consent is the most careful, respectful and ethical form of consent. It
requires the data collector to give participants a reasonable and accurate
understanding of how their data will be used.
Uninformed
data subjects may have their data taken from their social media platforms, however
Ofcom found that 65% of users accept terms and conditions without reading them,
so many users may not understand the extent of data usage.
Reference:
https://blog.hurree.co/the-ethics-of-big-data
Privacy
The ethics of privacy involve many different concepts such
as liberty, autonomy, security, and in a more modern sense, data protection and
data exposure.
- The concept of big data privacy:
- The condition of privacy
- The right to privacy
- The loss of privacy and invasion
An example of a significant data leak that caused a loss of privacy to over 200 million internet users happened in January 2021. A Chinese social media site called Sociallarks suffered a breach a hacker was able to access and scrape the database which stored:
- Names
- Phone number,.
- Email addresses,
- Locations,
- social media account login names.
Reference: https://bigdata-dialog.ch/en/the-main-ethical-legal-and-social-challenges-of-big-data/
Social Challenges
Big Data Divide: is the asymmetric relationship
between those who collect, store, and mine large quantities of data (usually
companies), and those who are the target of data collection (e.g., customers).
Recommendation: legislation should identify realistic harms
that could result from Big Data divide and develop legal safeguards for those
who are disadvantaged by the divide.
Reference: https://bigdata-dialog.ch/en/the-main-ethical-legal-and-social-challenges-of-big-data/
Discrimination and Big Data: Data bias can
potentially lead to discrimination and unfairness in machine learning. However,
the definition of what counts as bias is not only a technical matter, but a
normative choice.
Recommendation: Anti-discrimination policies must be
flexible enough to legitimate different statistical standard for different use
cases
Reference: https://bigdata-dialog.ch/en/the-main-ethical-legal-and-social-challenges-of-big-data/
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment